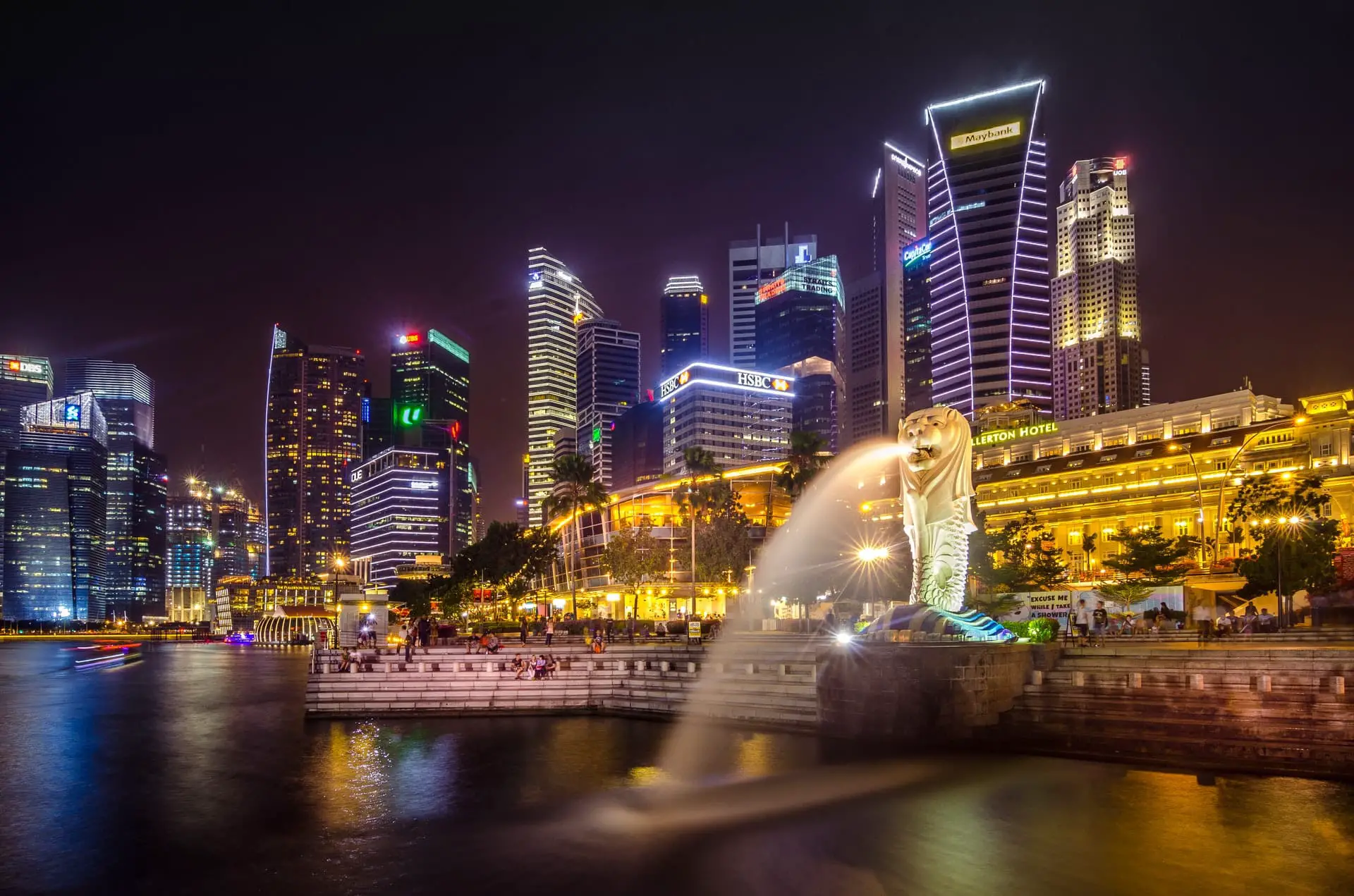
Everyone has heard about Singapore. This small island in Asia is making headlines as one of the strongest economies in the world. Along with Hong Kong, an autonomous region of China, Singapore is on the top list with a free economy.
So, you might be wondering, is Singapore in China? Is it the same with Hong Kong and Taiwan, two of China’s strongest regions?
No, geographically speaking, Singapore is not part of China. Nor is China’s overseas island. Singapore is a sovereign nation in Southeast Asia. It has its own governing rules regarding the economy, politics, culture, and religion. Further, Singapore is considered the largest port in Southeast Asia. Its port is one of the busiest on the globe. The growth enjoyed by Singapore is due to its strategic location near the Strait of Malacca. The strait is one of the busiest trading routes globally and connects the Indian Ocean to the South China Sea.
As you can see on the map, the small island is geographically blessed because of its proximity to trade. It is in the southern part of the globe and far from China, East Asia.
List of Contents
What country owns Singapore?
So, what country owns Singapore if it is not part of China? As I have mentioned earlier, Singapore is an independent country since 1965. It has endured a long-standing past dated back to the 14th century.
Before we came to know Singapore as a strong economy, the country underwent a transition. It was formerly part of the Johor Sultanate, which is associated with Malaysia.
During the intense colonization of Great Britain, Singapore became a colony. Sir Thomas Stamford Raffles negotiated a treaty with Johor Sultanate. It made Singapore a part of the British crown colony in 1918.
The island became a new port because of its strategic location. It is near the Strait of Malacca and in proximity to India and China’s main trade route. It was an ideal colony for Great Britain. The intent to make Singapore the new port was beneficial to Great Britain. It replaced the Netherlands as the dominant power in the southeast.
In World War II, Singapore was occupied by the Japanese Empire. Singapore reverted to British control after the war. During this time, the same with other colonies globally, the island has given the change to self-govern. The year 1963 was crucial to Singapore. It merged with the Federation of Malaya and became Malaysia. Disputes and unrest happened to lead to the expulsion of Singapore from Malaysia. It gained independence in 1965. After its secession, intense poverty confronted Singapore.
There are severe unemployment and housing crisis on the island. These pushed leaders to have stronger economic policies. An intense modernization program was implemented, including the establishment of manufacturing and infrastructures. The country was able to sustain growth and progress in the early 1990s. At present, Singapore is a member of the Commonwealth being a colony of Great Britain. It is now a top maritime capital in the world. It can be attributed to its colonial years, as it was established to be a port to transport goods to the west.
What is Singapore’s relationship with China?
Even before the period of colonization, Singapore and China already established a relationship. In the aspect of trade and commerce, both countries were good trading partners.
There is a large number of Chinese in Southeast Asia during the pre-colonial years. They are often called ‘Asian Jews’ because they swarmed around different parts of Asia.
Most of these Chinese settled in Southeast Asia were merchants who built businesses. Today, they generally control businesses in Malaysia, Singapore, Thailand, and the Philippines.
In Singapore, the Chinese flocked to the country during the active and lively opium trade. Remember, during that time, Singapore is considered a new port. The maritime trade route between China and India was vast and open. Singapore, as the new port, received most of the trade. It was able to establish a commercial relationship with the Chinese.
Since then, the Chinese began migrating to Singapore. Chinese now compose the majority of the island’s population.
At present, Singapore and China enjoy a cordial and diplomatic relationship. China is considered Singapore’s largest trading partner. At the same time, Chinese is Singapore’s largest foreign investor. They even established the China-Singapore Free Trade Agreement in 2009.
Today, there have government-to-government projects, including the following:
China-Singapore Suzhou Industrial Park
Sino-Singapore Tianjin Eco-City
China-Singapore (Chongqing) Demonstrative Initiative on Strategic Connectivity
China-Singapore Guangzhou Knowledge City
Singapore and China are two separate states that have diplomatic relations. Yet, China does not own Singapore. Only the majority of its population is of Chinese descent.
Why are there many Chinese in Singapore?
When you visit Singapore, you will notice that Singaporeans are of Chinese features. Most of them, young and old, have physical characteristics like the Chinese.
So, you might be wondering, why are there many Chinese in Singapore?
As I mentioned earlier, the Chinese compose the majority of Singapore’s population. Most of them migrated from Guangdong and Fujian provinces, the southern part of China. They were initially merchants and traders who married locals and found a settlement there. They even established Chinatown in Singapore.
The growth of the Chinese population in Singapore started in the 1980s. They initially went to Southeast Asia to establish trade. Once Singapore become the new port, and the opium trade was active, they settle in Singapore. As a result, they established different Chinese groups in Singapore. They are the following:
Hokkien
They are the largest Chinese migrants in Singapore. They came to the island to trade as what most of the Chinese did during that time. The Hokkien group were active merchants in Southeast Asia even before colonization. By the start of 1980, around 43 percent of the Singapore Chinese population is Hokkien.
Teochiu
Teochiu is another Chinese group in Singapore, comprising almost 22 percent of the Chinese population. The Teochiu came from the northeastern Guangdong Province. Like other Chinese who came from the southern part of China, this group came to trade and do business. They speak a dialect different from Hokkien.
Cantonese
The group came from the lowlands of Central Guangdong. They are merely 16 percent of the Singapore Chinese population. Like the other group, they are also traders and merchants who settled on the island.
Why do Singaporeans speak Chinese?
The biggest contribution of Chinese migration to Singapore is the language. There are a lot of Singaporeans who speak Chinese. It is a result of the migration process that happened in the 1980s and continues to increase now.
We all know that when a group of people migrates, they bring with them their local language. They continue to use it and even grow very rapidly once they multiply and populate.
Today, Chinese is widely spoken in Singapore. Yet, it is not the official language of the country. Malay is constitutionally the language of Singaporeans.
Mandarin is the chosen language for Singapore Chinese. It is promoted as the main language instead of Hokkien, Cantonese, and Teochiu. The government of Singapore had a campaign promoting Mandarin in 1980. The schools and institutions even use the language as a medium for Chinese students.
The use of Mandarin is a result of providing Singapore Chinese cultural identity. Today, most Singaporeans are bilingual. You will notice that many of them speak Chinese and English as well. Both languages are mediums of instruction in school.
Singaporeans consider themselves Chinese?
Chinese in Singapore is the majority race. It is not considered as a nationality. Many Singaporeans are of Malay descent. Some get offended when called Chinese.
Some Singaporeans do not want to be identified as Chinese. The same with Singaporean Chinese, who still want to be identified as of Chinese ancestry.
When you visit Singapore and interact with the locals, you have to be cautious about identifying them. Even though they look like Chinese, there are still dissimilarities you will see. Chinese are not only the majority group there. There are Malays, Indians, Singaporean Malay, Singaporean Chinese, and other minorities.
You will see that Singapore is a melting pot of cultures. There are cultural differences that can easily be noticed. Even in the subway, there are stations like Little India, Chinatown, and Bugis. You will see here varying cultures and lifestyles.
When you visit Little India, it will take you to India in Singapore. It is an ethnic district in Singapore located in the eastern part of the Singapore River. The aroma of Indian cuisine will greet you once you get out of the subway. The lines of marigold necklaces and incenses are present. You will be greeted by Indians offering you items and souvenirs while you are walking the street. There are Hindu temples, particularly the famous Veeramakaliamman Temple, practicing Hindu beliefs.
On the other side, there in Chinatown. The place where the vast cheap marketplace in Singapore is located. The place in itself transports you to China. Chinatown is a maze of narrow roads with lots of things to see. On one side, you can see Chinatown Food Street. The area is filled with traditional Chinese food like rice and noodles. On the other side, souvenir shops filled the streets. You can have cheap finds and deals just walking along the busy street of Chinatown.
The Bugis station in Singapore is the usual hang out place of Singaporeans of Malay descent. The neighborhood of Bugis and Kampong Glam is a mixture of race and culture. You can see mosques and Arabian street on one side during the Malayan Heritage Center on the other.
Singapore embraces many ethnicities. Being a major port then and now, it is a hub for a lot of races. You can easily identify them as they flock together to specific districts in the country.
There are parts of Singapore that are industrialized, like the Marina Bay area. You will see varying people roaming around in the city center, taking pictures in the lion city.
Singapore is culturally diverse. Singaporeans like to be identified based on nationality. They have distinguishing characteristics that they want you to take notice of and consider. It will not be hard if you respect their differences once you visit the country. After all, you wouldn’t want other people as a member of a different race.
Which country has the most Chinese immigrants?
Chinese is the biggest population around the world. There are over one billion Chinese on the globe, and 50 millions of them are overseas.
Even before China became a powerful economy, the Chinese established the settlement in different states. Most of them are living in Southeast Asia. There are old rich Chinese in these countries. As a breakdown, 75% of these overseas Chinese are in Singapore. The minority of the population settled in Malaysia and Thailand.
When China made itself one of the strongest economies, a wave of migration happened. You can see Chinese almost everywhere. Most of them are tourists who can spend a huge amount of money in various locations.
They are everywhere. Chinese are both in developed and developing countries. They have businesses, and the Chinese own even real estate. But a large number of them are in Singapore.
Yet, we must be extra cautious about identifying them as Chinese and not Singaporeans. Most of them wanted to be part of the race and not an ethnic majority. The language they speak is mostly Mandarin. It is the same with the full-blooded Singaporeans.
There may be a lot of Chinese in Singapore, but the latter is not part of China. Singapore, as a government, has its policy when it comes to the Chinese majority. The state strictly implements it to established cultural identity among many races living.